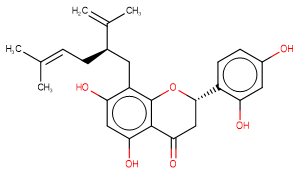
Sophoraflavanone G
CAS No. 97938-30-2
Sophoraflavanone G( Kushenol F | Vexibinol )
Catalog No. M21472 CAS No. 97938-30-2
Sophoraflavanone G (Kushenol F) isolated from Sophora flavescens induces MDA-MB-231 and HL-60 cells apoptosis through suppression of MAPK-related pathways.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 86 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 149 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 287 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 430 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 618 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSophoraflavanone G
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSophoraflavanone G (Kushenol F) isolated from Sophora flavescens induces MDA-MB-231 and HL-60 cells apoptosis through suppression of MAPK-related pathways.
-
DescriptionSophoraflavanone G (Kushenol F) isolated from Sophora flavescens induces MDA-MB-231 and HL-60 cells apoptosis through suppression of MAPK-related pathways.
-
In VitroSophoraflavanone G (0 -100 μM; 24 hours) decreases the viability of the HL-60 cells?in a dose-dependent manner.Sophoraflavanone G (0 -100 μM; 24 hours) induces HL-60 cell apoptosis, activated caspase-3 and caspase-9, and downregulated Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL. It also upregulates Bax and released cytochrome?c from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm, enabling apoptosis via the mitochondrially-mediated "intrinsic" pathwaySophoraflavanone G (0 -40 μM; 24 hours) inhibits MDA-MB-231 cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 value of29.7 ± 5.2μM.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsKushenol F | Vexibinol
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorApoptosis
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number97938-30-2
-
Formula Weight424.5
-
Molecular FormulaC25H28O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (588.94 mM)
-
SMILESCC(C)=CC[C@H](Cc(c(O[C@@H](CC1=O)c(ccc(O)c2)c2O)c1c(O)c1)c1O)C(C)=C
-
Chemical Name4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one 23-dihydro-57-dihydroxy-2-(24-dihydroxyphenyl)-8-(5-methyl-2-(1-methylethenyl)-4-hexenyl)- (S-(R*S*))-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Li ZY et al. Sophoraflavanone G Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukemia Cells and Blocks MAPK Activation.Am J Chin Med. 2016;44(1):165-76.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Elesclomol
Elesclomol (STA-4783) is a small-molecule oxidative stress inducer.
-
Silvestrol aglycone
Silvestrol is a potential anticancer rocaglate derivative from Aglaia foveolata, induces apoptosis in cancer cells through the mitochondrial/apoptosome pathway.
-
JHU395
JHU395 is an orally-bioavailable prodrug of a lipophilic glutamine antagonist (GA), 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine (DON).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


